If you are a student trying to apply to Canadian universities then you might have heard about SDS and non-SDS. The cycle of applying for a visa to get one is a time consuming process. But here we are going to simplify everything for you. Explore what actually SDS and non-SDS stand for, how they are different from each other, visa application for both and tips for successfully getting a visa. Do not forget to finalize the student accommodation in Canada before shifting there since students face challenges while finding accommodation.
What is SDS?
SDS stands for student direct stream, and was initially known as students partner program (SPP). It was initiated by Immigration, Refugee and Citizenship Canada for making the process of student visa as easy as possible. Did you know that Canada is one of the easiest countries to get a work visa?
Coming to the point, the most important thing to notice is that for the SDS category only the students belonging from Antigua and Barbuda, Brazil, China, Colombia, Costa Rica, India, Morocco, Pakistan, Peru, Philippines, Senegal, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Vietnam, Trinidad and Tobago countries are eligible to apply for now. The process from applying for a visa to getting the visa is pretty easy with the SDS approach.
So, if you are a student from any of these countries then this opportunity is for you to study in the best cities of Canada!
What is non SDS?
Non SDS is a general category visa process and that is why it takes longer to get a visa through non SDS approach. But the main feature about non SDS is that those who are ineligible for the SDS approach can apply for a visa through the non SDS category. The requirements for non SDS are also different from the SDS. Let’s dive into the blog to know more about the differences and many surprising facts.
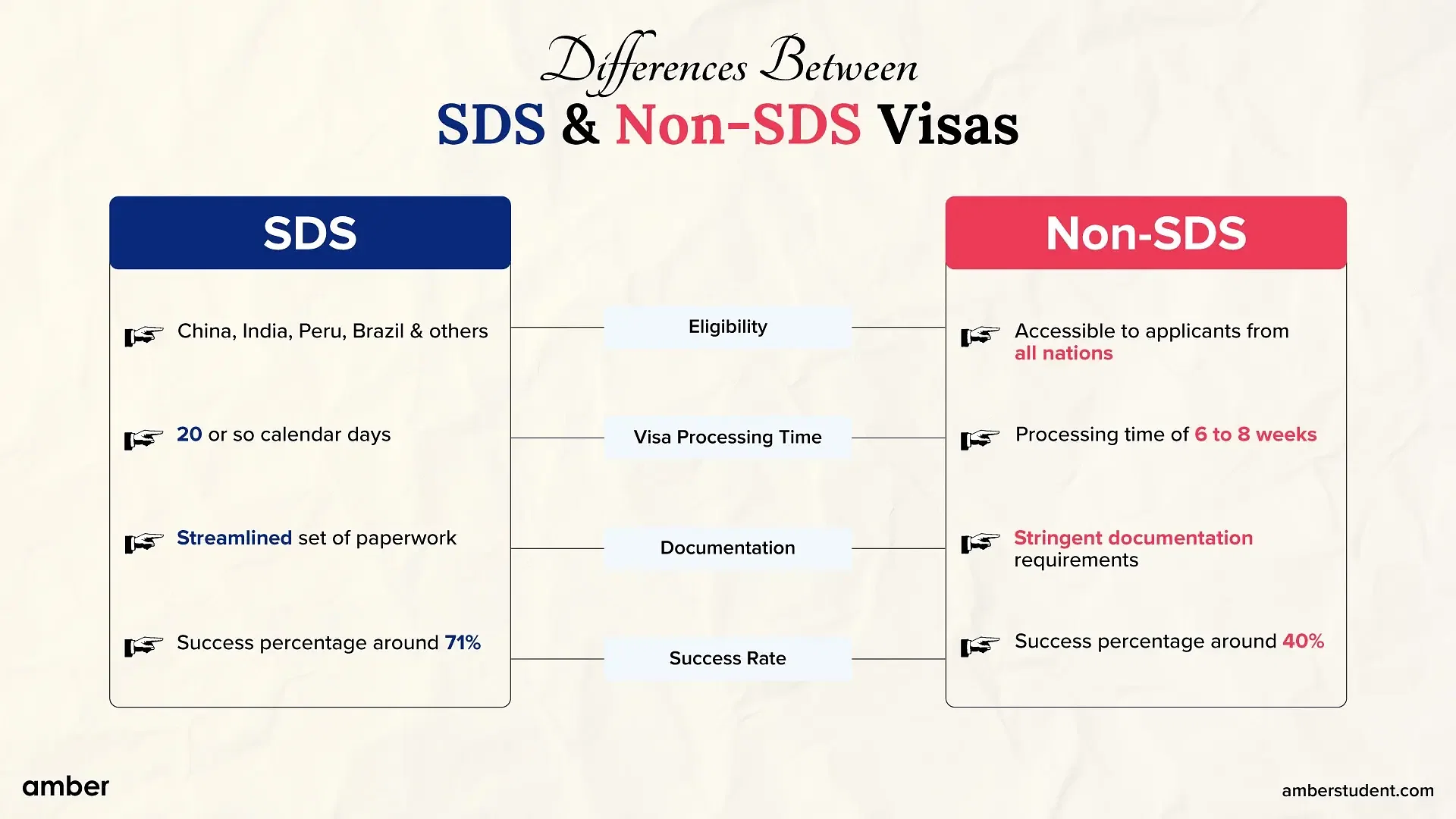
SDS vs non SDS
Understanding the distinctions between non-SDS and SDS visa applications is crucial when thinking about pursuing graduation or masters in Canada. While non-SDS visas are designed to accommodate a wider range of reasons like job, study, or immigration, the SDS programme offers an express-entry visa application process that is only available to students.
Eligibility: Specific nations as mentioned above including China, India, Peru, Brazil and others, are eligible for SDS visas. Non-SDS visas, on the other hand, are accessible to applicants from all nations.
Visa Processing Time: In terms of processing speed, applying through the SDS programme offers a sizable advantage. SDS visas often take 20 or so calendar days to process, giving students extra time to organise their courses and travel. On the other hand, non-SDS visa applications often take longer, with a processing time of 6 to 8 weeks.
Documentation: Compared to non-SDS visas, SDS visas often require a more streamlined set of paperwork. It's crucial to remember that the particular requirements could change depending on the applicant's circumstances and country of origin. Applications for non-SDS visas may be subject to more stringent documentation requirements that encompass several facets of the applicant's background, including educational credentials, professional experience, and financial capabilities.
Success Rate: Compared to non-SDS applications, SDS visa applications often have a greater success percentage. The success percentage for SDS visas now stands at around 71%, which indicates a positive outcome for a sizable portion of applicants. However, the success rate for non-SDS visas is roughly 40%; this number may change based on the circumstances of each applicant and the strength of their application.
So, what do you think is better? Well, read the whole blog for better clarity.
All about the SDS visa application
In this section, we'll go into detail about the prerequisites and the step-by-step procedure for applying for an SDS visa, giving you a thorough overview to help you get through the procedure.
Language ability test results: In order to be eligible for the SDS category, applicants must demonstrate their English language ability by receiving a minimum score of 6.0 bands or higher on the IELTS Academic or IELTS General test in each part. This requirement guarantees that students have the language proficiency needed to succeed in their academic endeavours. Here are the tips and tricks to crack the IELTS entrance exam!
Passport: A crucial prerequisite for a Canadian student visa is a current passport. Make sure your passport is valid for a long enough time; otherwise, Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) may be unable to provide you a study permit or other necessary paperwork.
Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC): SDS applicants must deposit CAD 10,000 or more as a Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC) in order to ensure financial stability and pay for additional fees. This sum acts as a safety net, giving students access to more resources and security in Canada. GIC alternatives are provided by participating banks like NOVA SCOTIA, ICICI, CIBC, and SBI, with the money being available after the applicant arrives in Canada.
Tuition fee: The first-year tuition charge must be paid in full in order to submit an SDS visa application. The Designated Learning Institution (DLI), an official letter of confirmation from the DLI, or a bank receipt demonstrating the transfer of monies to the DLI's repository account are acceptable forms of supporting documentation for payment submitted by applicants.
Letter of Acceptance: The first step in the SDS application process is to get a Letter of Acceptance from a Designated Learning Institute (DLI). International students can enrol in programmes at DLIs that have been approved by provincial and territory administrations. Getting accepted into a reputable DLI is necessary to get a study permit.
Educational Records: It is required to submit true and full educational records. These could include transcripts from the most recent secondary or post-secondary education, diplomas, graduation certificates (if applicable), and certificates for the 10th and 12th grades.
Medical Exam: Candidates must pass a medical examination performed by a panel doctor approved by the Canadian government. The upfront medical confirmation document is proof that you have the essential health conditions to study in Canada.
Statement of Purpose: Writing a strong Statement of Purpose is crucial to the success of your SDS visa application. The SOP should provide details on your profile, interests, and aspirations and explain why you choose a particular programme and college in Canada. Focus on your selected course and academic background in your SOP as you adjust it to meet the standards of the Canadian High Commission.
Digital Picture: It's crucial to include a digital picture that complies with the requirements established by the Canadian authorities. The image should be 35x45 in size, appropriately framed, and have an 80% zoom on a white background.
The SDS application must be filed online if you want your study permission to be processed more quickly. It is crucial to collect and arrange all required papers in digital format, attentively follow the directions in the application form's tutorial, and have a working credit or debit card on hand to pay the application fee. You can also be needed to visit an official website, pay a charge, and submit your biometric data there.
Coming to the non SDS visa application
Don't worry if you didn't meet the SDS requirements; Non-SDS is here to help. For students looking for a student visa to study in Canada, it's the hip alternative. Consider it your entry ticket for a brief stay in Canada. Prepare to investigate a brand-new application procedure that opens doors to your Canadian aspirations.
Language competency test: To prove their language competency, candidates must pass a test such as the IELTS, PTE, or TOEFL.
Passport: A current passport is required in order to apply for a student visa. Make sure your passport is not about to expire because this could prevent the study permit and temporary resident visa from being issued.
GIC: Students must deposit a Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC) for at least $10,000 Canadian dollars or more. This guarantees Canada's financial stability and gives extra money for spending. A few banks that provide GICs are SBI, ICICI, NOVA SCOTIA, and CIBC.
Tuition fee: Applicants must show documentation of paying the designated learning institution's (DLI) tuition for a period of six months. Financial stability must be demonstrated.
Medical Exam: Applicants must submit the necessary papers as proof of passing a comprehensive medical exam.
Academic Documents: Valid academic records, such as diplomas and transcripts from prior degrees, must be supplied.
Digital Photos: Applicants must submit digital photos that adhere to certain specifications, such as background colour and size.
Statement of Purpose: For a non-SDS visa application, a strong Statement of Purpose (SOP) is essential. It should detail why you decided to continue your education in Canada as well as the specific subject you want to take.
Financial Documents: To establish financial stability, financial documents such as evidence of income (Income Tax Returns, Form-16, J-Forms), bank statements, fixed deposits, and other liquid assets should be supplied.
Follow the CIC Canada application procedure to apply for the non-SDS visa. This entails setting up an account, figuring out your eligibility, supplying the necessary data and supporting documentation, reviewing your application, and then submitting it. Do not forget to pay the $150 application cost for a visa.
You can apply for the non-SDS visa by meeting these requirements and following the application procedure, and then start your journey to study or work in one of the best countries abroad.
Which visa option is right for you?
When planning your journey to study in Canada, selecting the appropriate visa option is essential. Let's examine the two primary choices SDS and Non-SDS and determine which is the best fit for you.
Fast Track to Success with Student Direct Stream (SDS)
If you fit the requirements and want a streamlined, quick process, SDS may be the best option for you. SDS is ideal for students who want to start their Canadian journey right away because it offers speedier visa processing dates.
Opportunities and Flexibility in Non-SDS
The Non-SDS option gives flexibility and the ability to pursue your aspirations of obtaining a Canadian education for people who might not be able to meet the strict requirements of SDS. More people can apply for a student visa under Non-SDS, giving you more chances to pursue your academic goals in Canada.
However, the Student Direct Stream (SDS) stands out for a number of compelling reasons, such as the faster application procedure, the need for fewer documents, and the program's ability to speed up the typically 20-day visa processing time. Apply for SDS if you are short on time and study in Canada’s amazing universities like University of Toronto!
Tips for SDS and non-SDS visa success
You can obtain a visa with success! Increase your chances of success with these insider tips for SDS and non-SDS visas:
1. Understand the requirements like a pro
Become familiar with the particular specifications of the SDS and non-SDS visa programmes. The requirements for each programme are different and must be met. You can increase your chances of receiving a visa by making sure you have the required paperwork and meet the eligibility requirements by thoroughly comprehending the requirements.
2. Strongly prepare your supporting documents
Supporting documents are required for both SDS and non-SDS visa applications to demonstrate your eligibility and financial stability. Make sure you collect all the necessary paperwork, including acceptance letters from designated learning institutions (DLIs), educational transcripts, financial statements, and results of language proficiency tests. Your application is strengthened and your readiness is demonstrated by presenting thorough and precise documents.
3. Consider getting professional direction and assistance
Immigration consultants or educational agents can analyse your application documents, offer insightful feedback, and give suggestions on how to make a strong case to the visa officers. Their knowledge and experience can increase your chances of success and remove any doubts or difficulties you might experience.
Understanding your visa choices is essential for a successful journey to Canada to study. If you are interested in knowing more about Visa, read our blogs on Canadian student visa and visa guides for study in Australia and the USA. Good luck with your visa application and have fun on your fascinating academic journey in the Great White North!




.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




